Description
La ecuación de estado de Redlich – Kwong está dada por
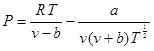
donde R = constante universal del gas [ = 0.518 kJ/(kg.K)], T = temperatura absoluta (K), P = presión absoluta (kPa), y v = volumen de 1 kg de gas (m3/kg). Los parámetros a y b son calculados por
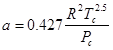 ,
, ![]()
donde Pc = presión crítica (kPa) y Tc = temperatura crítica (K). Como Ingeniero Químico, se le consulta para determinar la cantidad de metano combustible (Pc = 4600 kPa y Tc = 191 K) que puede ser almacenado en un tanque de 3 m3 a una temperatura de –40°C con una presión de 65000 kPa. Use un método de localización de raíces de su preferencia para calcular v y luego determine la masa de metano contenido en el tanque.
The Redlich – Kwong equation of state is given by
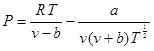
where R = the universal gas constant [ = 0.518 kJ/(kg.K)], T = absolute temperature (K), P = absolute pressure (kPa), and v = the volume of a kg of gas (m3/kg). The parameters a and b are calculated by:
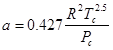 ,
, ![]()
where Pc = critical pressure (kPa) and Tc = critical temperature (K). As a Chemical Engineer, you are asked to determine the amount of methane fuel (Pc = 4600 kPa and Tc = 191 K) that can be held in a 3 m3 tank at a temperatura of –40°C with a pressure of 65000 kPa. Use a root – locating method of your choice to calculate v and then determine the mass of methane contained in the tank.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.